Sinus Cancer Doctor in Kolkata

Symptoms of Sinus Cancer
Common symptoms of Sinus Cancer include:
- Persistent nasal congestion or blockage (usually on one side)
- Nosebleeds
- Facial pain or swelling
- Reduced sense of smell
- Vision changes
- Lump or mass inside the nose or mouth
If you have experienced any of these signs, contact the sinus oncologist in Kolkata for immediate diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Sinus Cancer
Tobacco Use
Alcohol Consumption
Chronic Sinus Infections and Inflammation
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection
Radiation Exposure
Previous radiation treatment to the head and neck for other conditions or cancers may increase the risk of developing sinus cancer.
Genetic Factors
While there’s no specific genetic mutation identified as a direct cause, a family history of cancers can sometimes predispose individuals to sinus cancer or other head and neck cancers.
Environmental Pollutants

Stages of Sinus Cancer
Stage 0: Carcinoma in Situ
Stage I
Stage II
Stage III
The tumour has either:
- Invaded further into nearby bones or tissues, like the eye socket, or
- Spread to a nearby lymph node (often still smaller than 3 cm).
Stage IV
-
Stage IVA:
The tumour has invaded deeper structures (like the skin, the orbit of the eye, or the base of the skull) and may involve lymph nodes larger than 3 cm but not larger than 6 cm.
-
Stage IVB:
The tumour may involve critical structures, like the brain or the deeper parts of the skull, and could have spread to multiple lymph nodes or larger lymph nodes.
-
Stage IVC:
The cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the lungs, or other parts of the body.
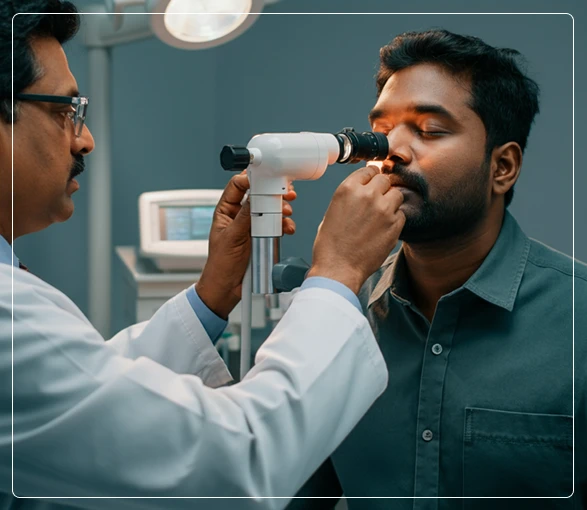


Diagnosis of Sinus Cancer
Medical History and Symptoms Review
- The doctor will begin by taking a detailed medical history, including any symptoms you may be experiencing.
- A discussion about risk factors, such as tobacco and alcohol use, and any family history of cancer will also be important.
Nasal Endoscopy
A nasal endoscopy allows the doctor to visually inspect the nasal cavity and sinuses using a thin, flexible tube with a camera (endoscope). This procedure can help identify any abnormal growths or areas that may need further examination.
Imaging Tests
-
CT Scan (Computed Tomography):
This scan provides detailed cross-sectional images and is particularly useful for identifying the tumour’s size, location, and any bone involvement.
-
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
MRI is often used to look at soft tissue structures and can help distinguish between cancer and benign sinus conditions. It’s especially useful for examining tumours close to the eyes or brain.
-
PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography):
A PET scan may be ordered if there’s a need to check for potential spread of the cancer to other parts of the body.
PET/CT Scans
Types of Biopsies :
-
Endoscopic Biopsy:
During a nasal endoscopy, a tissue sample is collected from abnormal areas.
-
Needle Biopsy:
If the tumour is accessible, a thin needle may be used to collect tissue.

Treatments of Sinus Cancer
Radiation Therapy
-
External Beam Radiation:
High-energy beams are directed at the tumour to destroy cancer cells. It may be used as a primary treatment or as an adjuvant therapy to eliminate cancer cells.
-
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT):
IMRT delivers precise doses to minimise damage to surrounding healthy tissue, which is critical for head and neck cancers.
Chemotherapy
Targeted Therapy
Immunotherapy